
Overview of Burnett

The Burnett region is a fertile area, with several major river systems including the Nogo, Stuart, Burnett, Boyne and Auburn Rivers.
The region spans an area of 34,515km² and currently is home to around 144,700 people. The Burnett region as covered by this Regional Drought Resilience Plan, stretches from Kalpowar in the north, Bundaberg in the east, across to Mundubbera and Eidsvold to the west. The southern limits of the Burnett region reach to Benarkin. The Traditional Owners of the Burnett region include the Bailai, Gurang, Gooreng Gooreng, Taribelang Bunda, Wakka Wakka, Kabi, Kabi, Burunggam and Wuli-Wuli peoples. The region encompasses the four local government areas (LGAs) of Bundaberg, North Burnett, South Burnett and Cherbourg. Bundaberg is the major regional centre, with principal centres including Kingaroy and Gayndah.
As with most of Australia, there is a strong link between water – the waterways, waterholes and the patterns of rain and flood – in this region and the cultural practices of First Nations peoples. The region is particularly susceptible to flash droughts that typically last for as little as a month, or up to six months.
Past impacts of drought in this region
Past impacts | People, culture & community
EXTRACTS FROM THE FULL RDRP PLAN
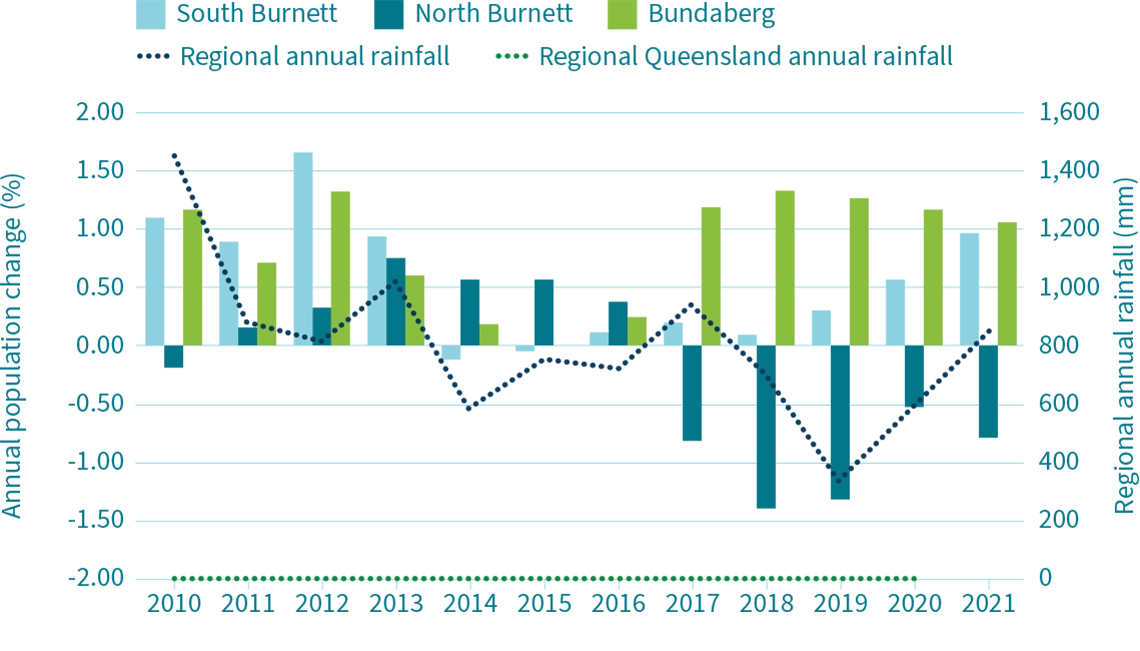
For the people living in the Burnett region, drought has a negative impact on several key elements of their wellbeing.
Respondents during drought rated their sense of community economic wellbeing; overall community wellbeing; access to and availability of support services; and state of Natural Capital as lower during times of drought.
In addition, it has been noted that drought exacerbates chronic stresses and underlying issues such as:
- legal and financial problems
- medical and health problems
- alcohol and substance abuse
- isolation and social withdrawal
- breakdown of relationships
- in the worse cases, self-harm and suicide.
These individual stresses, in turn also influence (and are influenced by) the collective wellbeing effects on communities and landscapes – in effect, drought can create a cycle of stress and decline in mental health.
Past impacts | Economy
EXTRACTS FROM THE FULL RDRP PLAN
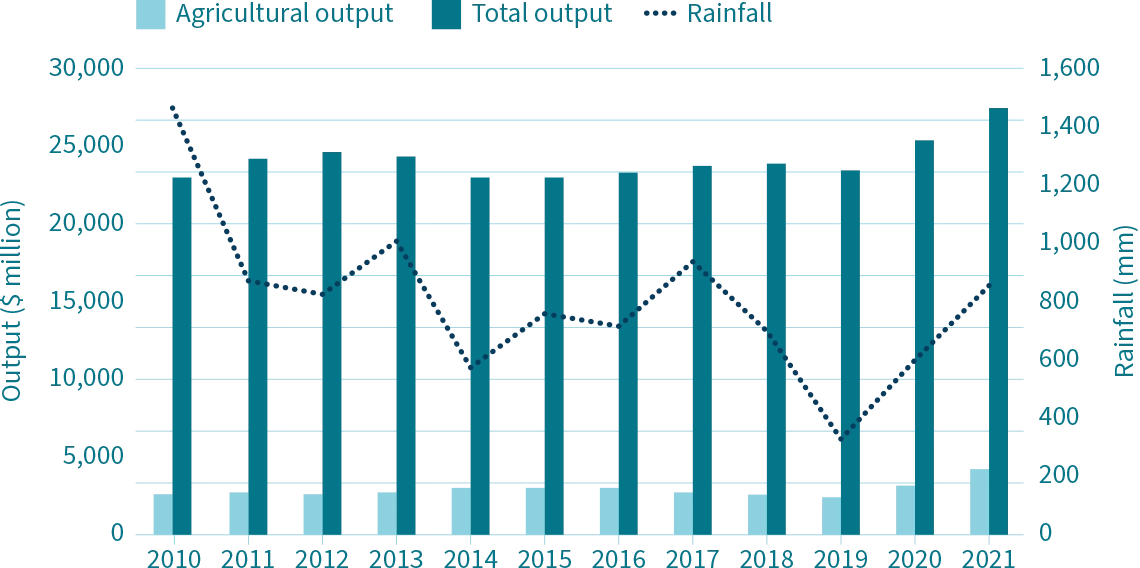
During periods of drought, the Burnett often shows a decrease in economic output.
In fact, there has been a correlation with decreases in the region’s Gross Regional Product (GRP) during drought. This is the case particularly for the North Burnett area, whose reliance on agriculture makes its economy particularly vulnerable. Recent droughts have driven financial and land management practice change in many farming enterprises in the region. However, according to surveys of the region, only an estimated 36% of farmers had a written farm plan with business objectives. Of those plans 79% included drought strategies and 88% included other farm risks. In addition, farms in the Morton to Curtis region (encompassing the Burnett region) have been recorded as profitable for only two years from 2005-2020.
"In this area the impact of drought has been exacerbated. It has been cumulative the things that have knocked people around. Not just the droughts but the floods too. These combined have meant that a lot of places around here have cash issues and will be going into this next drought without much of a buffer."
Rural financial counsellor
Past impacts | Landscape and natural environment
EXTRACTS FROM THE FULL RDRP PLAN

Traditional owners of the land feel the multi-faceted impacts of drought on the landscape of the Burnett region and the effect it still has on their communities.
Many of the people working on the land also note the changes as a result of drought in the area: a shorter growing season, damaged topsoil and a land too damaged to take in water.
Both published research and land manager’s observations also identify drought results in mobilisation of sediment (topsoil) from paddocks to water ways. This has a negative impact on both land and wetland conditions. For the waterways, high levels of water extraction leading into and during dry times also potentially reduces water quality, thus placing further stress on aquatic ecosystems.
In conjunction with lower water quality, several aquatic species are also facing elevated water temperature, which can have negative effects on species’abundance.
"Traditional owners still use the waterways for subsistence, education, general life – fish for crabs, mullet, fish. Spend time in river to reconnect with spirt and teach young people – dry rivers have spiritual & mental health impacts. Waterholes dry up. Drought impacts their medicine plants and other native plants they eat. When [First Nations] people get to their country and see it in a degraded state it has a great impact on them.”
NRM manager
Past impacts | Infrastructure and built environment
EXTRACTS FROM THE FULL RDRP PLAN
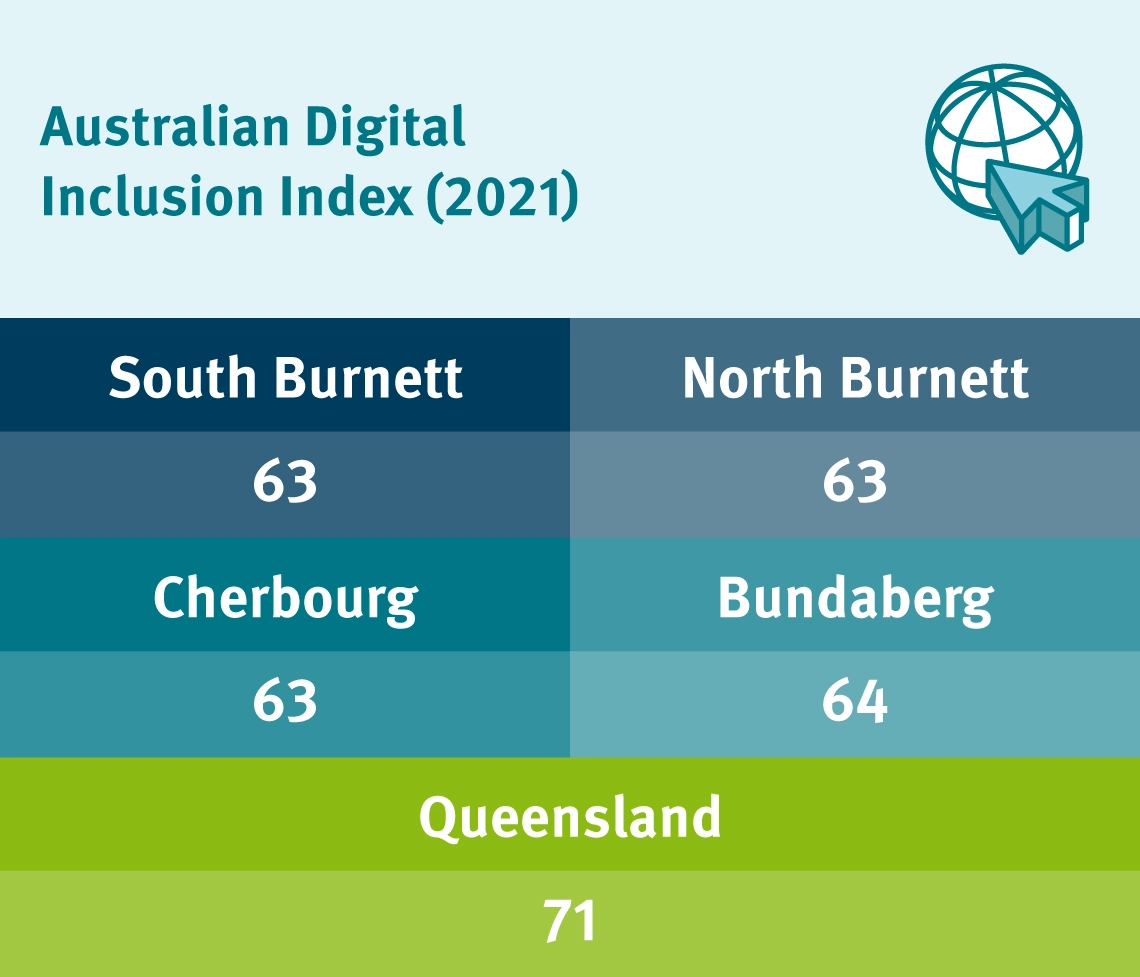
Burnett’s hard and soft infrastructure are both impacted by drought.
However, there is an opportunity to build improved regional drought resilience in Burnett through increasing the utilisation of existing water storages.
A particular priority for improving Burnett’s drought resilience is building more reliable and effective digital infrastructure. Even in locations with internet connectivity, reliability remains an issue. A majority of agricultural producers state their connection is unreliable and they depend on expensive satellite services.
The Burnett region also has an extensive road network which deteriorates during drought. During times of drought, the inadequacies of the road network are more evident. In fact, one participant in surveying suggested that the poor road network may have discouraged the establishment of further feedlots in the region.
"Effective telecommunication networks are important, not just for keeping in touch and doing business, but during times of disruption. Our network of townships need reliable telecommunication infrastructure and back-up power supplies to prepare, respond and recovery from disruptions. Quality communication sets us up for success at other times too, creating opportunities for new, digital business ventures and remote working.”
Burnett Regional Resilience Strategy, 2023
Likely future impacts of drought in this region
Future impacts | People, culture & community
EXTRACTS FROM THE FULL RDRP PLAN

Likely effects of future drought on communities in the Burnett region may include:
- local out migration
- exacerbated local issues
- mental health issues and suicide
- loss of expertise and experience with regard to agricultural and landscape knowledge and practice
- loss of volunteers and participants in community events.
Future impacts | Economy
EXTRACTS FROM THE FULL RDRP PLAN

Likely effects of future drought on the economy in the Burnett region may include:
- reduced availability/diversity of local employment
- decreased investment in the region
- diminished borrowing capacity
- loss of sequestered carbon stock
- increased insurance premiums.
Future impacts | Landscape and natural environment
EXTRACTS FROM THE FULL RDRP PLAN

Likely effects of future drought on the landscape and natural environment in the Burnett region may include:
- damage or loss to crops due to heavy rain ending drought
- permanent wilting point exceedance due to increased evapotranspiration
- prolonged or flash droughts leading to crop failure
- reduced pasture conditions
- damage or loss to livestock
- dehydration of landscape
- reduced dissolved oxygen and fish kills due to soil and surface water oxygenation
- damage or loss to soil due to heavy rain ending drought
- increased likelihood of bushfires
- loss of key links or species due to increased mean temperatures and reduced adaptive capacity
- reduced condition or loss of vegetation
- increased in-stream habitat sedimentation.
Future impacts | Infrastructure and built environment
EXTRACTS FROM THE FULL RDRP PLAN

Likely effects of future drought on the infrastructure and built environment in the Burnett region may include:
- increased load on ICT services and data
- increased demand on water infrastructure.
Regional strategy
Regional strategy | People, culture & community
EXTRACTS FROM THE FULL RDRP PLAN
Planning and monitoring
Projected outcome: Plan for drought responses, implement drought monitoring and early warning systems.
Respond to drought events
Projected outcome: Manage responses during drought by dealing with impacts, vulnerability and risk.
Build future resilience
Projected outcome: Implement resilience measures to limit future impacts of drought and better respond to drought.
Regional strategy | Economy
EXTRACTS FROM THE FULL RDRP PLAN
Planning and monitoring
Projected outcome: Plan for drought responses, implement drought monitoring and early warning systems.
Respond to drought events
Projected outcome: Implement resilience measures to limit future impacts of drought and better respond to drought.
Build future resilience
Projected outcome: Support activities known to promote future resilience.
Regional strategy | Landscape and natural environment
EXTRACTS FROM THE FULL RDRP PLAN
Planning and monitoring
Projected outcome: Plan for drought responses, implement drought monitoring and early warning systems.
Respond to drought events
Projected outcome: Manage responses during drought by dealing with impacts, vulnerability and risk.
Build future resilience
Projected outcome: Implement resilience measures to limit future impacts of drought and better respond to drought.
Regional strategy | Infrastructure and built environment
EXTRACTS FROM THE FULL RDRP PLAN
Planning and monitoring
Projected outcome: Plan for drought responses, implement drought monitoring and early warning systems.
Respond to drought events
Projected outcome: Manage responses during drought by dealing with impacts, vulnerability and risk.
Build future resilience
Projected outcome: Implement resilience measures to limit future impacts of drought and better respond to drought.